I. Introduction of liquid liquid extraction(LLE)
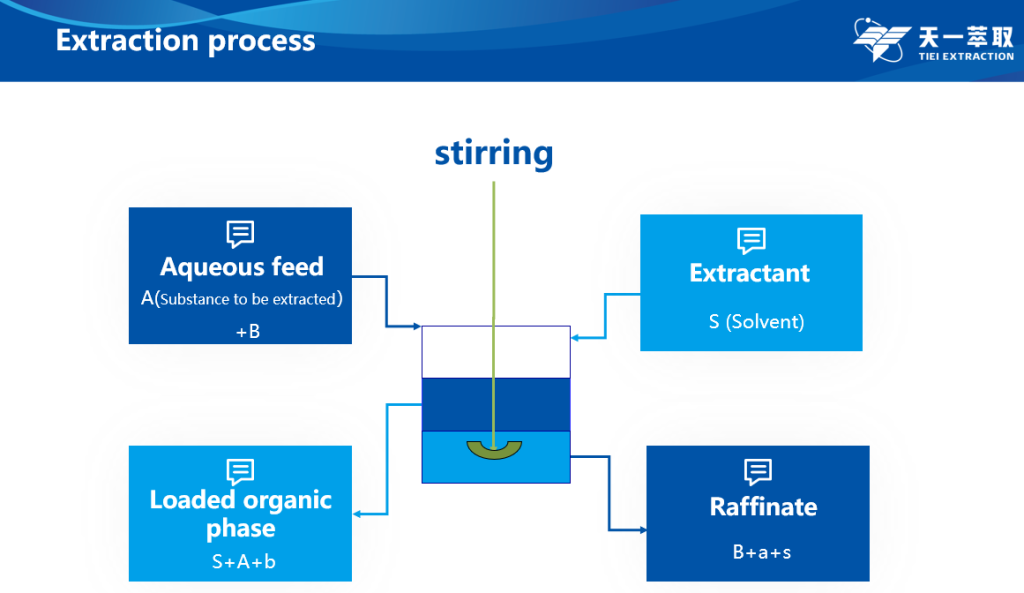
Liquid Liquid Extraction is also called LLE, also known as solvent extraction. It is a method of transferring solutes/substances(A) from Aqueous feed to another immiscible solvent(S) by utilizing the differences in solubility or partition coefficients of substances in two immiscible (or slightly soluble) liquids.
Technical Terms related to liquid-liquid extraction:
- Aqueous feed: The liquid which contain the extracted material originally.
- Organic phase: Composed of extractant and diluent.
- Extractant: An active organic reaction agent that can combine with the extract and transfer into the organic phase in the form of an extract.
- Diluent: A low density organic solvent that dissolves extractants. It is an inert solvent that does not react with metals, usually a mixture of various low aromatic alkanes, such as kerosene.
- Extraction phase and raffinate: The organic phase after extraction and layering is called the extraction phase (loading), and the aqueous phase at this time is called the raffinate (residual water)
- Scrubbing(washing): The process of washing impurities (including encapsulated aqueous phase) from the organic phase to the aqueous phase, while the extracted substance remains in the organic phase
- Scrubbing /washing agent: Solvent for washing extraction phase (load) containing impurities
- Loaded organic phase: After washing, separation and layering , the organic phase is loaded organic phase
- Raffinate:The aqueous phase after extraction.
- Back-extraction(stripping): The process of returning the extracted substance to the aqueous phase by adding a new aqueous phase that does not contain the extracted substance and contacting the extraction liquid.
- Back-extraction/stripping agent: solvent used for back-extracting the solutes in the washed loaded organic phase
- Back-extraction solution: The organic phase after stripping and layering is referred to as poor organic phase
- Poor organic phase: The water phase at this time is called the back extraction solution(back-extraction water)
II. Application of Liquid liquid extraction:

Liquid-liquid extraction is widely used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical engineering,hydrometallurgy, environmental analysis, and food processing for purposes like purification, separation, and concentration of substances.
III. Liquid liquid extraction methods
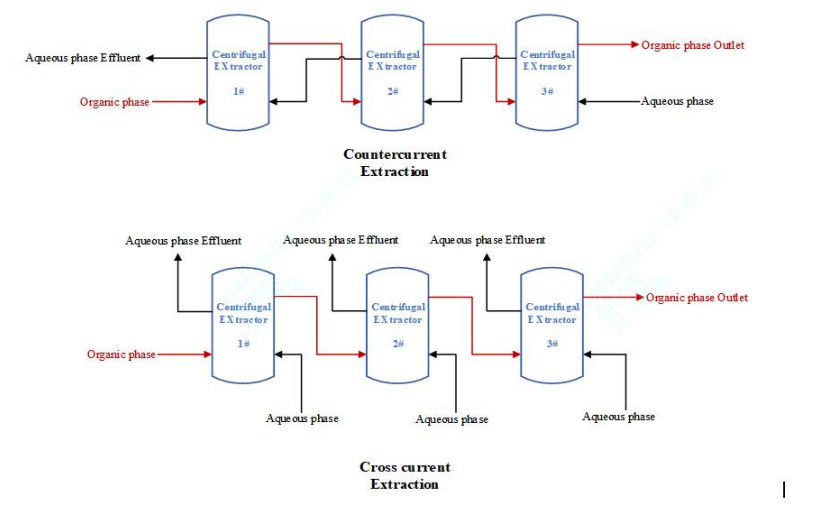
The two main process of liquid liquid extraction is : Multi-stages Continuous Countercurrent Extraction & Multi-stages Continuous Cross Current Extraction.
IV. Equipment used in liquid liquid extraction process:
Mixer-Settlers: Mixer-settler units consist of mixing chambers where the two liquid phases are brought into contact and settling chambers where they separate based on density differences. This type of equipment is commonly used for solvent extraction in hydrometallurgical processes.
Centrifugal Extractors: Also known as centrifugal contactors, these devices use centrifugal force to enhance the mixing and separation of liquids. They are effective for high-throughput liquid-liquid extraction processes.
Others: like exraction column, Membrane Extraction system etc.
V. Liquid liquid extraction steps:
- Solvent selection: When design an liquid liquid extraction plant, the first step is to select the extractant(solvent) which is immiscible with the aqueous liquid , and has a high affinity for the target substance to be extracted.
- Mixing: mixing the solvent and aqueous phase togethers and agitating, to make two phases contact sufficiently.
- Phases separation: the aqueous phase and organic phase will be separated by natural gravity or centrifugal force(depends on the equipment you used) according to their different densities.
- Washing: You may need a washing step to remove the impurities, then make sure the purity of extracted compounds.
- Stripping: also called back-extraction, it is the reverse process of extraction. The process of using a reverse extractant to return the extracted substance from the loaded organic phase back to the aqueous phase.
- Drying/evaporation: If needed, remove any water or residual solvent from the extracted compound by evaporating.
Welcome to consult TIEI EXTRACTION for more information about liquid liquid extraction(LLE)!