In industrial production such as chemical industry, energy, and mining, the operation of separating liquid mixtures is often involved, in which a liquid solvent (extraction agent) that is insoluble or partially miscible with the liquid mixture (mixed liquid) to be separated is added to form a two-phase system. The operation of utilizing the differences in the distribution of each component in the mixed liquid between the two phases to allow more of the soluble components (solute) to enter the solvent phase (extraction phase) to achieve separation is called liquid-liquid extraction.
In order to improve the recovery efficiency of target products, most liquid-liquid extractions in industrial production adopt countercurrent operation mode. Countercurrent extraction mode can be divided into multi-stage countercurrent extraction and continuous countercurrent extraction.
- What is multi-stage countercurrent extraction? What equipment does multi-stage countercurrent extraction mainly include?
Mixer settlers and centrifugal extractors are typical multi-stage countercurrent extraction equipment. The principle is that the light and heavy phases in each stage of extraction equipment achieve phase balance as much as possible through the co-current mode, and then after phase separation, they enter the two stages of extraction equipment before and after the equipment in the opposite direction. Therefore, in a multi-stage extraction process, the extraction efficiency can be improved by increasing the number of stages to achieve the target yield.
- What is continuous countercurrent extraction? What kind of extraction equipment is typical for continuous countercurrent extraction?
Column equipment such as pulse extraction column is typical continuous countercurrent extraction equipment. Its principle is that the light and heavy phases enter the equipment from the upper and lower ends respectively. Under the action of external force fields such as gravity or centrifugal force, the light and heavy phases flow relatively countercurrently. At this time, the dispersed phase is dispersed into droplets and turbulent through pulse or stirring to complete the mass transfer operation between the two phases.
- How to choose these two extraction equipments? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
① Compared with multi-stage countercurrent extraction, the advantage of continuous countercurrent extraction is that multiple theoretical levels can usually be achieved in one device; but the disadvantages are also very obvious: due to the countercurrent flow of the two phases, the relative shear force between the phases is relatively large, which makes the dispersed phase droplets easily entrained by the continuous phase, resulting in backmixing. When the two-phase flux is large and the droplets are small, backmixing is more serious and eventually leads to liquid flooding and failure to operate normally. This limits the application of continuous countercurrent extraction equipment in engineering.
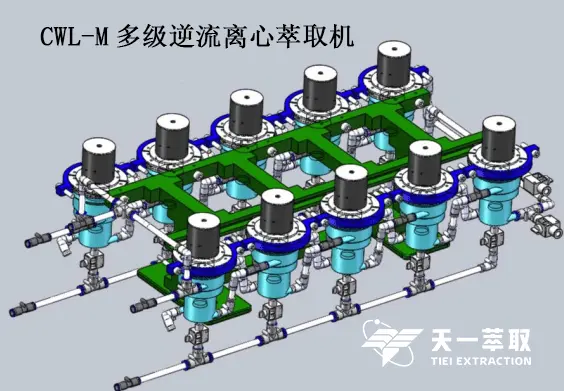
② Multi-stage countercurrent extraction is introduced using a centrifugal extractor as an example. CWL-M series centrifugal extractor, first of all, uses the principle of centrifugal force to separate very quickly and has a larger processing capacity. Secondly, optional materials include polytetrafluoroethylene, stainless steel, PP materials, etc. to meet different corrosion resistance requirements. These are completely different from column devices such as pulse extraction columns.
In practical applications, the choice of which extraction equipment needs to be determined based on specific extraction requirements and conditions. Multi-stage centrifugal countercurrent extraction is suitable for situations with large processing capacity and high separation requirements. Factors such as equipment footprint, separation speed, and material corrosion resistance also need to be considered.
More details welcome contact us. Email: sales@tieiextraction.com